In this blog post, we’ve targeted all eCommerce store owners, offering a step-by-step guide to setting up your first Google Ads campaign. Focusing on practical tips 101 to boost traffic and conversions, these include: optimising keywords, writing compelling ad copies, and others to kick off your first Google Ads campaign.
Now that you have your eCommerce store up and running, you should now shift your focus onto driving traffic to your online store. The ticket to this fast track is Google Ads (previously known as Google AdWords), Google’s very own advertising service that allows you to strategically position search results for your site on a search engine results page by paying for them. Google Ads offers many benefits to eCommerce store owners, these include:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Having a massive reach of 5 billion searches per day
- Fast performance
- Maintaining full control of your campaigns constantly and more.
Google Ads provides you with the perfect opportunity to rank on top of the SERP while harnessing intent.
What’s Google Ads?
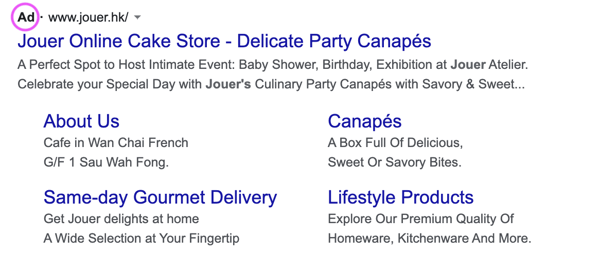
In a nutshell, here’s an example of what a paid ad would look like on Google:
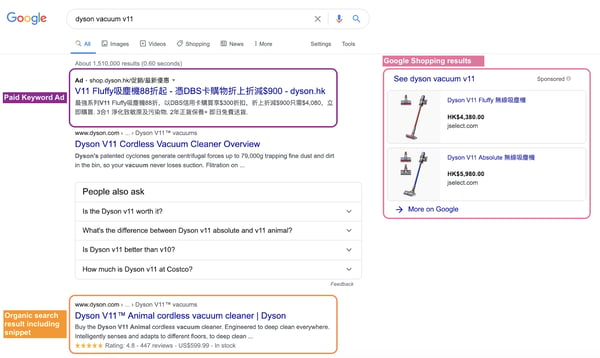
Google produces a list of searches instantly when you type in a particular term on Google Search. However, you will notice that the top few results are most likely paid ads (The ones that have “Ad” before the URL), and the ones below are organic search ads.
To start your Google Ad, you would need to understand some basic metrics to track the performance:
- Impressions. This is the number of times an ad is viewed.
- Clicks is the number of times your ad was clicked on by a user.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR). This is the percentage of users who clicked on your ad out of the total number of impressions it received. The higher the CTR indicates the higher your relevance.
- Cost Per Click (CPC). As Google Ads works using a dynamic bidding system, you as the advertiser will have to select a maximum bid amount that you’re willing to pay for a click on your ad. CPC is the amount that you pay for each click on your ad.
- Average Position. This is a statistic that describes how your ad ranks against other ads, also known as Ad Rank. It is determined by your bidding CPC, and also Quality Score, which is based on the quality and relevance of your ad.
- Conversion Rate (CVR). A conversion is a specific goal you are tracking, the CVR is a percentage of the number of conversions divided by the number of clicks.
Setting up your Google Ads
Now, after familiarising yourself with the above terms. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide to setting up your own Google Ads campaign.
Check out the video to start your Google Ads journey, or scroll down to view the text version!
Step 0: Setting up your first campaign
You will need to create your Google Ads account. Once you’re on the page, hit the “Get Started Now” button, then proceed to click on the “Create your first campaign” button.
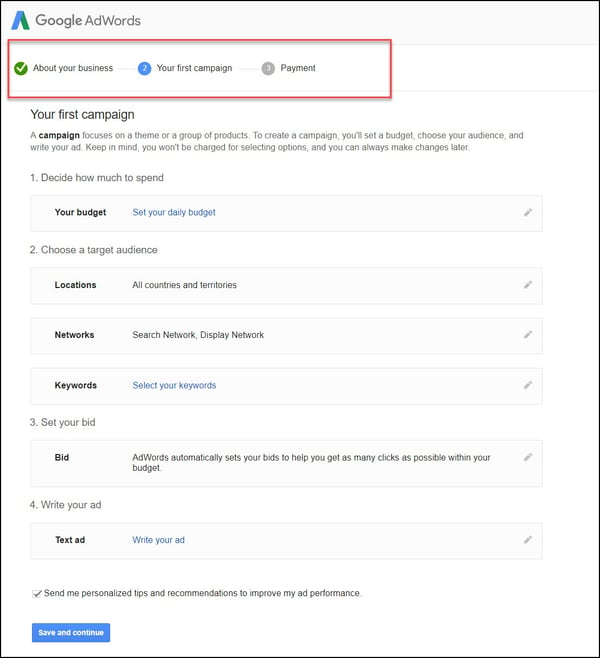
It might be overwhelming as you’re just starting out, but don’t worry, this article will address every part to building a successful campaign. All the elements in the above image will be explained throughout this article.
There are a variety of campaigns you can run using Google Ads, one being the Search Network. This article will focus only on the search network because it incorporates two huge factors: searcher intent and pay-for-performance that can fulfill your goals more effectively.
Step 1: Linking Google analytics, Google My Business Account and Google Merchant Center Account
You most likely already have Google Analytics set up on your website to track traffic, conversions, and other metrics. However, to better optimize your Google Ads campaign, you should also link your Analytics account to Google Ads. This will reduce time spent on tracking, analyzing, and reporting between multiple channels and campaigns as all of these events will be in one place.
Another opportunity to boost your local business is to link your Google My Business Account into your Google Ads campaign. We’ve also provided practical tips for SMEs to set up and maximise the use of a Google My Business Account, and how it can help benefit local businesses. This will allow you to take advantage of your location within your Google Ads. The ads will include an address extension, a pin for Google Maps, and higher visibility to pop up against ads that don’t have a local advantage.
You can also link your Google Merchant Center account. This will enable you to take advantage and maximise the benefits of retail-centric Google Ads campaign tools to improve your presence on the web -which is very important. You can set up Google Shopping Ads using the product data feed from Merchant Center, it can also be used for dynamic remarketing and local inventory ads, which we will talk about in more detail in our future blog content.
Step 2: Figuring out your budget and bid
As a beginner, it is recommended to set a lower daily budget. This way, it enables you to start at a steady pace and gather data along the way. You can monitor your campaign performance and further optimize on your future campaigns. To easier help calculate your budget, you can use a Maximum CPC formula:
Maximum CPC = Average Order Value x Average Profit per Order x eCommerce Conversion Rate
As your business grows, you can adjust your daily budget accordingly, however, you must take caution that Google can and will go slightly over your daily budget. Thus it is important to check on your campaigns to ensure that you don’t exceed your maximum monthly ad budget.
Don’t fret if you’re unsure what budget works best for your business. There are a few bidding strategies that can improve your performance depending on which stage your business is at:
Bid Strategy |
Level of Control |
Ease of Use |
Remarks |
|
Manual CPC -Advertiser setting own bid at keyword level. |
High |
Easy to use and modify |
We recommend that beginners or low budget businesses use manual CPC to avoid unprecedented fluctuations. This may be time consuming. |
|
Smart Bidding -Composed of a set of conversion-based strategies. Incorporates a range of auction-time signals like location, browser and time of day to design bids to suit the specific context of each search. |
Low |
Harder to use if not experienced with Google's machine learning and AI |
Although Smart Bidding can allow you to save time while achieving your performance goals, one must keep an eye on rising bids. |
|
Enhanced CPC -A form of Smart Bidding. ECPC partially automates your manual bids by adjusting your max CPC. |
Medium |
Medium as Google is taking some control over bids. |
Common outcomes are increased CTR, CPC and Conversion Rate. Because bids can adjust without a set ceiling automatically, one must take caution of this and always check for profitability. |
Step 3: Choosing your location
This is an important step as it plays a crucial part in your placement in the SERP. You’ll have to assess your target audience and create ‘rules’ that raise or lower bids based on where someone is searching from.
For example, if your business is only targeted towards the Hong Kong market, you will have to set Hong Kong as your location. If you’re looking to sell internationally as well, you may want to consider setting up several campaigns for those other countries, or where most of your buyers live. Another example would be if your store relies on foot traffic, deliveries and proximity, and you would prefer to target a location with a specific distance (e.g. 10km around your store), this can be set as well in the location settings and will help you geo-target your store to specified areas. This is essential when it comes to making the most out of a limited advertising spend.
Step 4: Brainstorm strategic keywords for your campaign
As Google Ads follows a pay-per-click (PPC) model, you’ll want to match your ad to the most relevant searches possible. This is to ensure that your keywords will match the searcher’s intent as much as possible.
.jpeg?width=600&name=WhatsApp%20Image%202020-06-30%20at%201.57.33%20PM%20(1).jpeg)
Here, it is very important to put yourself in the buyer’s position. Think about what is going through the buyer’s mind while they are looking to purchase your product. You may feel inclined to add as many keywords as possible as you think that would get you the most attention, however, don’t fall into this trap as you’ll only be spending more money on useless keywords.
A shortcut to this is to find long tail keywords for your market. Despite that long-tail keywords may have comparatively low search volumes, but collectively, they make up a majority of all online searches. Long tail keywords are easier to rank on, they can help you carve out your niche, and they also convert better.
If you’re lost at which keywords to use, you can start off with the Google Keyword Planner and start searching for keywords.
Once you’ve set your product category, the right country and language, you’ll be able to see the monthly search volume for keywords in that region, and the average CPC for each one. You can then see which keywords are better to cut down on and which ones to keep.
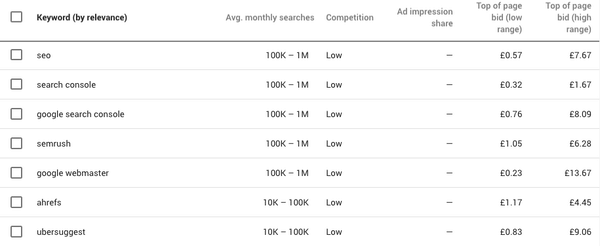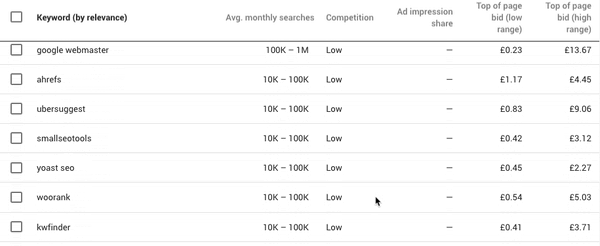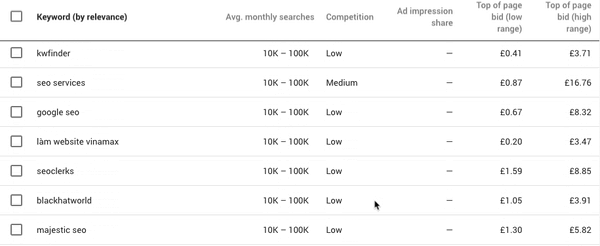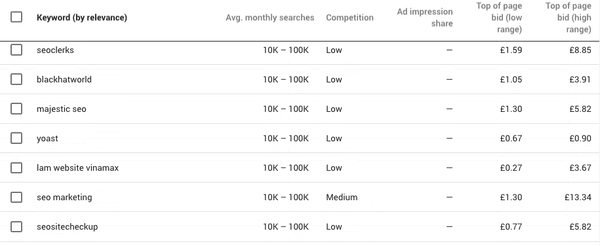
You’ll also want to know how your competitors are ranking for these keywords. It is important to understand what keywords your competitors are trying to rank for, this allows you to evaluate your own list of keywords. SEMrush helps you assess the types of terms your competitors are ranking for, they provide you with a number of free reports that show you the top keywords for domains that you enter.
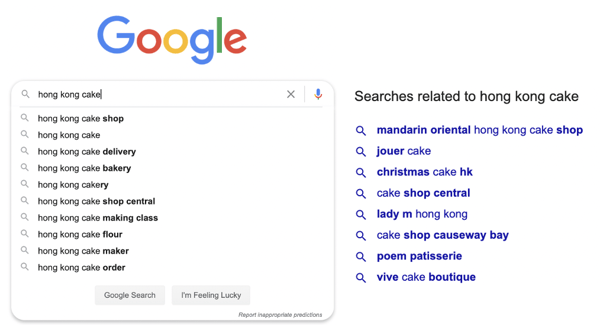
Other solutions to finding keywords or long tail keywords are to use Google Autocomplete and Google “Searches Related To…”. These can provide you with a better idea of what searches have been put into the search engine, and lets you know there is an audience for these keywords.
Other ways to optimize your campaign using keywords is to use Google Analytics to tell you what people are searching for already on your site. Another way is to take a look at Google Trends to see what specific places, people or locations are receiving more attention.
Lastly, Google Ads has four match types. Match Types tell Google how you want to match a search query. They are Broad match, Modified Broad Match, Phrase Match and Exact Match. You want to ensure that the correct Match Type is chosen for your Google Ad in order for your ad to be found. If you’re a beginner and are troubled about not knowing exactly how your buyer persona will be searching, you could move start with a more broad match to assess which queries yield the best results. Broad Match will pull in the widest amount of people possible, and Exact Match will pull in the smallest as it is more specific. It is always important to keep track with new information so that you can modify your ads accordingly.
Step 5: Writing a strong Ad Copy
Your Ad Copy includes a headline and description, it is crucial that your Ad Copy matches the searcher’s intent, is aligned with your target keywords and offers a feasible and clear solution to your persona’s problem. As your Ad Copy can be the deciding factor to whether your ad gets clicked on over your competitor’s ad.
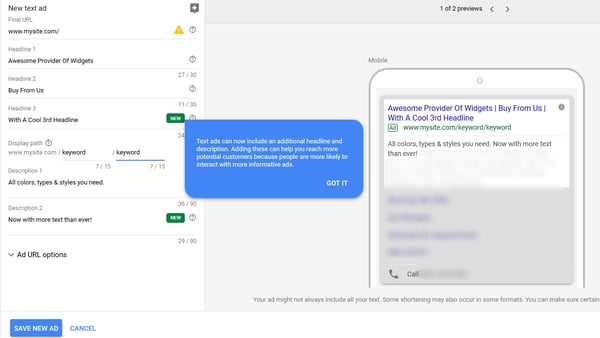
Writing a compelling “hook” and value proposition in your ad copy is necessary for your ad to get clicked on. To start with, there’s the headline. You have 25 characters to attract someone’s attention.
Your objective in the body copy is to get someone to understand what your offer is, and click through to learn more about it. Here you can focus on the key benefits of your product or service, describe any special offers, and end with a strong call to action.
Including a call-to-action (CTA) is essential when it comes to trying to boost click-through rate . The easiest way to get people to click on your ad is to ask them to do so. You could incorporate power words to trigger prospects to click. And it is important to note down that sometimes -less is more.
Step 6: Consider adding extensions
Here are just a few examples of extensions that could further push your conversion rates:
- Sitelinks extends your ad and helps you stand out in the competition and appeal to users by providing additional links to your site.
- Location extensions will include your location and phone number within the ad so that searchers can utilise Google Maps to find you easily. This works especially well for businesses with a physical store as their ad will come up in search query “...near me”.
- Call extensions allow you to include your phone number in your ad, this way users have an additional alternative to reach out to you immediately. If you have a customer service team ready to answer the phone, this is a perfect opportunity to engage and convert your audience.
You should definitely utilise ad extensions as they are free, and provide users with extra information to further interact with your ad and make your ad impactful overall.
Step 7: Tracking results for performance review and optimise for future campaigns
When it comes to performance review and checking to see how your Google Ads campaign is doing, these first few metrics are the first steps to keep an eye on so that you can optimise your future campaigns:
- Tracking your Click-Through-Rate: Whether you are engaging enough to achieve an action from your audience
- Tracking you Cost-Per-Conversion: How much it costs for you to get a customer
- Tracking your Average Position: How you rank against other ads
There are other metrics that you can observe to track your campaign’s performance, such as the bounce rate and conversion rate. However, as for now those will be introduced more in depth in our next blog post.
What happens now?
Now that you’ve had a step-by-step guide teaching you how to set up a Google Ads campaign, there is no excuse not to maximise this opportunity to help your business grow after setting up your own eCommerce store! Over time, it is important that you continuously check up on, maintain and improve your Google Ad campaigns. Create more ads and begin building your first ad groups, change what needs to be fixed and study the data. Get in touch with our eCommerce and digital marketing expert now if you need assistance in taking your first step in creating a Google Ad campaign!

